What are sleep substances?
Sleep substances, a general term for substances that appear in the brain and body fluids of sleep-hungry animals to induce or maintain physiological sleep, are a variety of candidates.
I cite and refer to the research paper 睡眠物質.
These are prostaglandin D2, adenosine, melatonin, interleukins and tumor necrosis factor (cytokines), oxidized glutathione and vitamin B12 and uridine.
Prostaglandin D2
Prostaglandins are a generic name for a series of biologically active substances (hormones) synthesized from arachidonic acid contained in biological membranes. One of these prostaglandins, prostaglandin D2 (PGD2), is produced in the brain and induces spontaneous sleep in rats and monkeys when administered in the brain. In humans, it has been reported that PGD2 levels increase 100 to 1000 as the disease progresses in African sleeping sickness caused by trypanosome infection, in which various neurological symptoms, mainly drowsiness and severe headache, appear after fever, headache, and muscle pain, etc.PDG2 is the most potent sleep inducer among endogenous sleep substances.
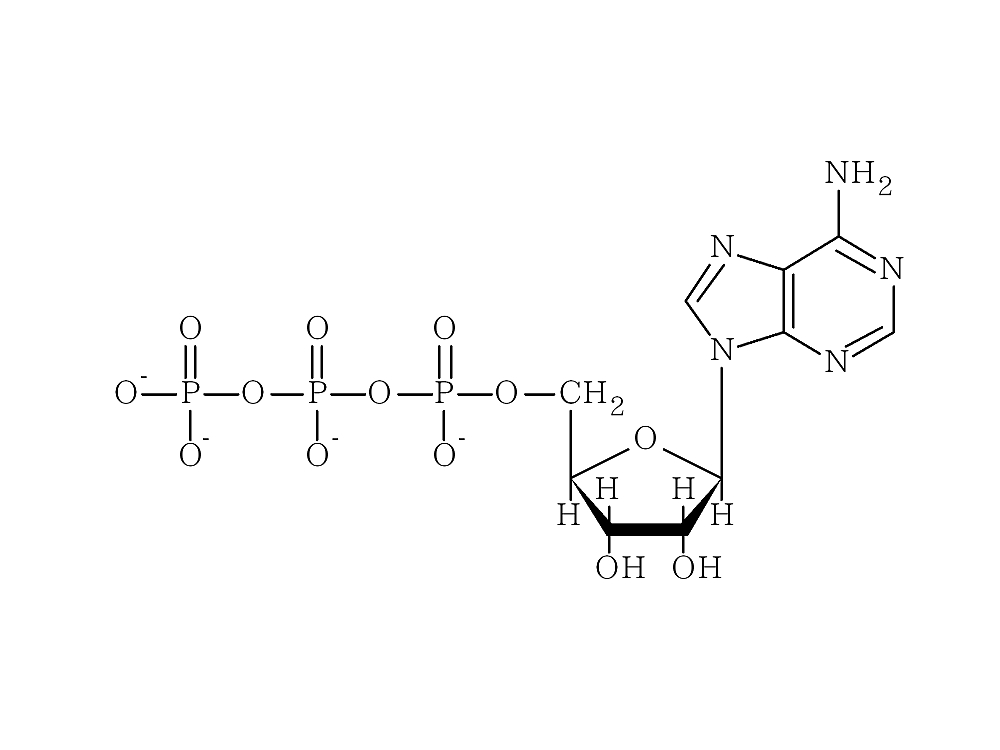
Adenosine
Adenosine is a compound consisting of adenine bonded to ribose. Adenosine administration into the ventricles of the canine brain in the 1970s induced sleep, and caffeine was proven to have arousing effects as an antagonist of the adenosine receptor. Adenosine is therefore considered to be a sleep substance. Adenosine is phosphorylated intracellularly and converted to ATP, which is the source of biological energy. When extracellular adenosine levels increase, energy is needed, and sleep facilitates the increase in ATP.
Melatonin
Melatonin is composed of tryptophan as a precursor via serotonin and N-acetylserotonin. As a treatment for insomnia, melatonin is administered to insomniacs who lack the ability to produce melatonin, and sleep is induced or qualitatively improved. Melatonin secretion is regulated by exposure to sunlight. This is because sunlight has served as a clock since time immemorial. Regardless of whether an animal is diurnal or nocturnal, melatonin synthesis increases at night and decreases during the day. Thus, melatonin is not a sleep substance in the strict sense of the term, but rather a clock substance.
Interleukins and tumor necrosis factors (cytokines)
Interleukin 1β (IL-1β) and tumor necrosis factor (TNFα) are cytokines that play important roles in inflammatory and immune responses. Sleep induced during bacterial and viral infections is thought to occur via the action of IL-1β and TNFα. There are five reasons for this (1) Administration of IL-1β to rabbits, rats, mice, cats, and monkeys increases slow wave sleep. (2) The amount of IL-1β mRNA increases in the brainstem and hypothalamus during the interrupted sleep. (3) IL-1β mRNA levels in rats have a diurnal rhythm and are highest during the daytime, which is the sleep period. 4) Substances that induce IL-1β expression, such as lipopolysaccharide, induce slow wave sleep, which is deep sleep. (5) Inhibition of endogenous IL-1β by neutralizing antibodies suppresses spontaneous sleep. TNFα also seems to induce sleep in animal experiments.
Oxidized glutathione, vitamin B12, uridine
Substances were extracted from the brains of sleep-deprived rats, and those obtained were oxidized glutathione, vitamin B12, and uridine. And, They have found sleep-inducing effects.
Glutamate is one of the amino acids that make up proteins and acts as an excitatory neurotransmitter. And oxidized glutathione induces sleep by inhibiting the binding of glutamate to its receptors and suppressing the excitatory nervous system.
Vitamin B12 has been reported to inhibit glutamate synthesis and, like oxidized glutathione, is thought to induce sleep by suppressing the excitatory nervous system.
Uridine is thought to induce sleep by binding to low-affinity sites on GABA receptors and activating the inhibitory nervous system.

コメント